Thoracentesis
Overview
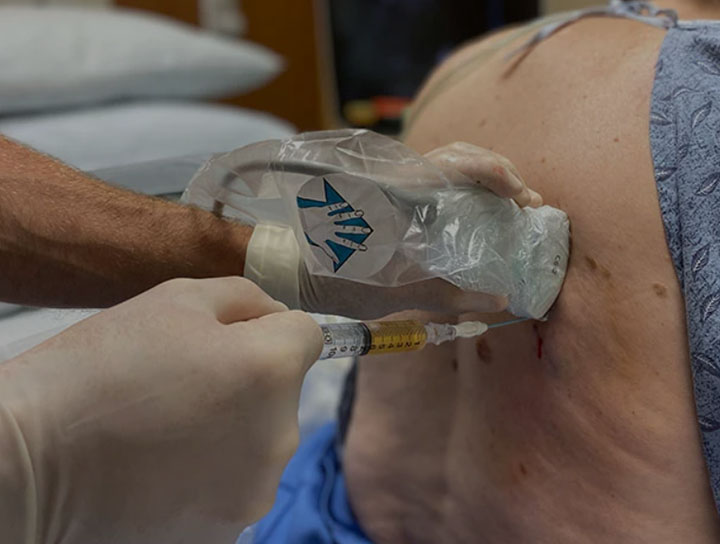
Thoracentesis is a procedure that a provider uses to drain extra fluid from around the lungs (pleural space) with a needle. It’s used to test the fluid for infection or other illnesses and to relieve chest pressure that makes it tough to breathe. Thoracentesis is a short, low-risk procedure done while you’re awake.
What is Thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis is a procedure that takes fluid out from around your lungs (pleural space). The pleural space is the area outside your lungs but inside your chest wall.
Your lungs and chest wall are both lined with a thin layer called pleura. A small amount of fluid between these two layers helps them move smoothly past each other when your lungs get bigger and smaller as you breathe. Just like a hinge needs oil to help the door move smoothly, your lungs need pleural fluid to help you breathe.
Some medical conditions and diseases cause fluid to leak into the pleural space (pleural effusion), which makes it hard to breathe. Healthcare providers use thoracentesis to test the fluid for diseases or to relieve symptoms.
Differences Between Procedures
What’s the difference between thoracentesis and paracentesis?
Thoracentesis removes fluid from your chest, while paracentesis removes fluid from your abdomen.
What’s the difference between a thoracentesis and a chest tube?
Thoracentesis drains fluid from your chest during the procedure, which usually lasts about 15 minutes. A chest tube, or a smaller drain with a curled end (pigtail catheter), stays inside your chest and drains fluid or air over a few days. It’s placed by a surgeon, pulmonologist, or radiologist.
Is thoracentesis a major surgery?
No, thoracentesis isn’t considered a major surgery. It is minimally invasive, meaning your provider doesn’t have to make large cuts in your tissue. Recovery time for minimally invasive procedures is short, and risks are much lower than for major surgery.
Who Needs Thoracentesis?
If you have a pleural effusion, you may need to have thoracentesis done to look for the cause or to make you more comfortable.
Why is Thoracentesis Done?
Thoracentesis is done either to relieve your symptoms or to test the fluid around your lungs (or both). Common reasons to have thoracentesis done include:
- Infection: If your healthcare provider thinks you have an infectious disease (like a bacterial infection) that’s causing pleural effusion, they’ll remove some fluid for testing.
- Cancer: If cancer may be causing pleural effusion, your provider can test your pleural fluid for cancer cells.
- Symptom relief: If pleural effusion is making it hard to breathe, your provider can remove some of the fluid to make you more comfortable.
What Does Thoracentesis Treat?
Thoracentesis treats pleural effusion, or excess fluid in the space between your lungs and your chest wall. It helps relieve symptoms and figure out what might be causing the fluid, so that your provider can treat it appropriately. Many underlying conditions cause pleural effusion, including:
